Microgrids
Microgrids can provide complete energy security by combining several energy sources to feed a building, campus or community. Utilizing clean energy enables microgrids to be a valuable tool for decarbonization and energy freedom.
Overview
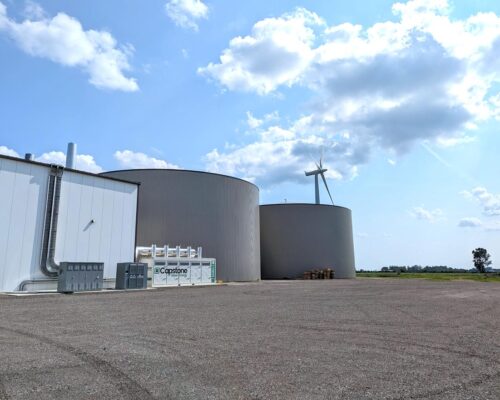
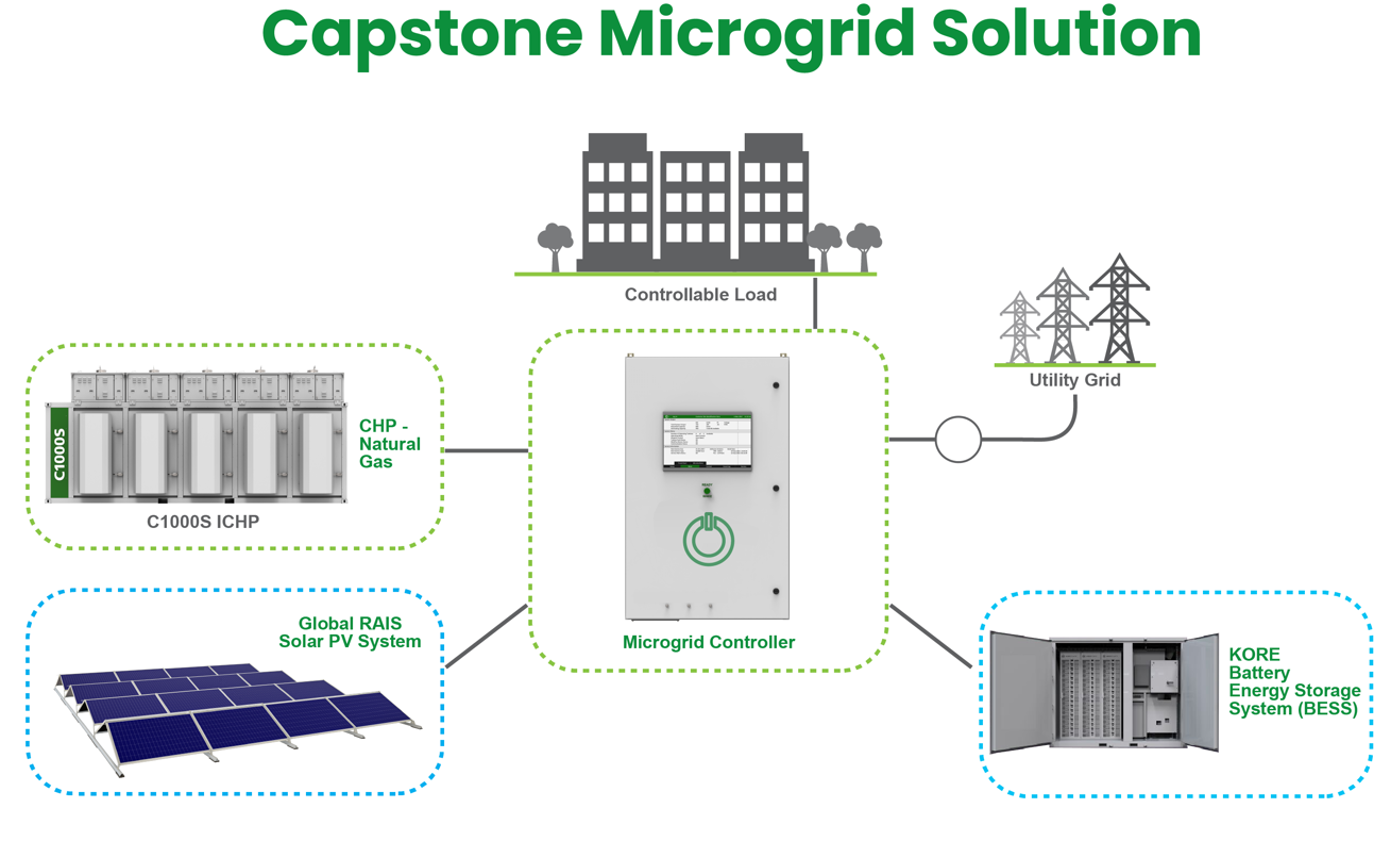
A microgrid is a distribution network that incorporates a variety of distributed energy resources (DER) that can be optimized and aggregated into a single system. The integrated system can balance loads and generation with or without energy storage and is capable of islanding whether connected or not connected to a traditional utility power grid.
Distributed energy resources typically include dual mode Capstone Microturbines, reciprocating engines, solar photovoltaic (PV), wind turbines, fuel cells and battery storage. Microgrids can be connected to larger electricity grids, and in the event of a widespread outage, can disconnect from the main grid to operate independently and supply electricity to homes and businesses that are connected to the microgrid’s electricity network.


The foundation for renewable energy microgrids
Key Benefits










Our energy experts deploy innovative technical solutions customized to our customers’ unique energy, business, and climate needs.
- We listen and understand
- We work with you, not just for you
- We design and build
- You save money and gain energy freedom
- We stay with you for the life of the project
- We treat you as our partner and always deal honestly and openly
- We keep you informed at each step, so that you’re always in control





